1.1 The Ecosystem of the
Natural Forest
The ecosystem of the natural forest is a perfect and complete
system. In the natural forest there are a huge number of species
of plants, animals and micro-organisms. Living (biotic) and
non-living (abiotic) things exist within certain relationships
and in a certain balance. The ecosystem describes the pattern
of relationships and interactions among living and non-living
things. Therefore, it is very important for us to understand
this first.
1.1.1 The Nutrient Cycle
(Regenerative System)
In ecology, all living things are placed in one of three
categories: producers, consumers or decomposers.
The main point of understanding the ecosystem is learning
the interaction between producers, consumers, decomposers
and other non-living things (sun, water, air, minerals, etc.).
Producers are plants
which have green leaves containing chlorophyll. They produce
food (carbohydrates) for themselves and all other living things
by using sun energy (the only energy from outside) and taking
nutrients (minerals, water, carbon dioxide, etc.). This production
process is called photosynthesis. It is very important to
note that nothing can produce food for living things except
plants. That is why they are called producers.
Consumers are animals
which live by eating the products (carbohydrates) of producers
directly and indirectly. Consumers are divided into four groups:
first order, second order, third order and top carnivorous
animals The first order includes herbivorous animals (e.g.
insects) which eat the products of the producers directly.
The second order are carnivorous animals (e.g. spiders, frogs)
which eat mainly animals of the first order. The third order
are carnivorous animals (e.g. snake) which eat mainly animals
of the second order. The top carnivores are animals (e.g.
eagle, tiger) which eat mainly animals of the third order.
No animals eat top carnivores. Man is categorized as a consumer.
(Note: The actual relationship among animals is more complicated.
This classification shows the basic relationship only.)
Decomposers
are micro-organisms (fungi, bacteria, virus, etc.) which live
by eating organic matter such as the waste of producers and
consumers(e.g. fallen leaves, dead body and dung of animals,
etc.). There are huge numbers of micro-organisms living in
the soil (more than 100,000,000 in 1 gram of fertile soil).
The most important function of decomposers is to change organic
matter into humus through decomposition and minerals through
mineralization. Humus is indispensable for making and improving
the soil. Minerals are absorbed again by producers as nutrients.
(From another angle, the work in the soil, the soil is kept
clean and healthy, otherwise, the surface of the planet would
be full of the waste matter of producers and consumers.)
As the diagram shows, the more producers (plants) produce
carbohydrates, the more consumers (animals) can live. The
more organic matter is supplied to the soil from producers
and consumers, the more decomposers (micro-organisms) become
active and the more nutrients are supplied to the producers.
The producers increase and more sunlight is used for carbohydrate
production. This system is called the nutrient
cycle.
It may also be called the carbon cycle, ni9trogen cycle,
mineral cycle, etc. The deference is in the focus. When the
focus is on carbon, then it is called the carbon cycle.
Through the nutrient cycle, all living things increase and
the soil becomes fertile. Every living and non-living things
interacts in nature-there is nothing useless or unnecessary.
They are all tied together in relationships of needing and
supporting one another. If one piece is disturbed, the whole
system reacts. For instance, if organic matter is not supplied
to the soil, micro-organisms (decomposers) become inactive
and the soil becomes infertile and plants (producers) cannot
produce well in the infertile soil. The low production of
producers consequently reduces the numbers of animals (consumers).
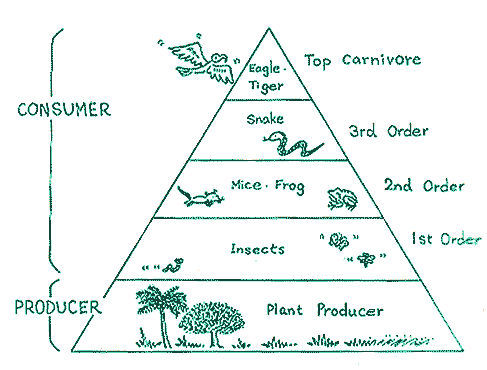
1.1.2 The Ecological Pyramid
The ecological pyramid is another perspective of the relationships
and balance between living things - especially consumers -
and how nature controls and balances the nubers in each group.;
The shape of the pyramid shows the allocation of numbers (bottom
to top large to small).
 |
|
The Ecological Pyramid
|
For instance, so-called harmful insect are consumers of
the first order. (herbivores) that eat producers (green plants)
directly. However the number of insects is controlled by consumers
of the second order,(bird, frog, spider, etc.) and kept within
certain limits. Therefore, the second are eaten by consumers
of the third order (snake etc.) and the third are eaten by
top carnivores (eagle, tiger etc.). In this way, each order
of consumer is naturally held to certain limited numbers by
the control of upper orders and quantity of food supply form
lower orders. Consequently, the shape of the ecological pyramid
is formed by the numbers of each order and the producer and
shows very clearly that basic foundation are the producers.
If the producers increase in number, the consumers can also
increase in numbers. But a decrease in producers results in
a decrease in consumers.
This relationship (eating and being eaten) between producers
and consumers is called the food chain. The food chin is an
ecosystem which is very delicately balanced and disturbances
at any one stage upsets this. For example, if snakes are destroyed
in large number for their skin, then mice and rats would proliferate.
If frogs decrease greatly in number for export of frog legs,
an increase in the population of insects and reduction in
crop yield would result.
|
1.1.3 The Important Rules for Agriculture
- The main source of energy for the production of
carbohydrates is the sun. Maximum utilization of sun
energy is most important for agricultural production.
- It is only green plants which can use sun energy
to produce carbohydrates. The degree of utilization
of sun energy is dependent on the quantity of green
plants.
- The source of fertility (minerals, humus etc.)
is organic matter which contains micro-organisms.
A supply of organic matter is indispensable for soil
improvement through fertilization.
- Every living thing interacts and there is nothing
which is unnecessary and harmful in nature.
|
|


